BCG instillations
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) is the main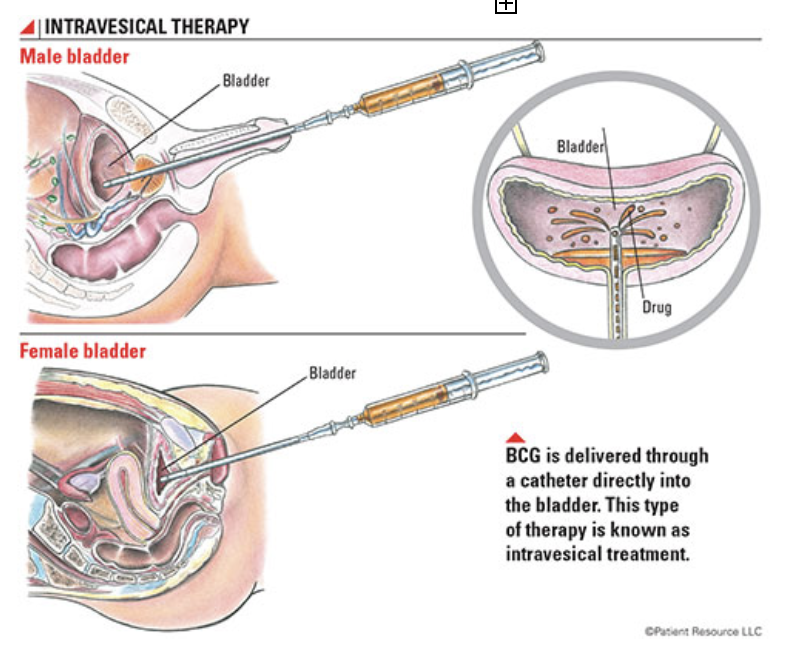 intravesical immunotherapy for early stage bladder cancer.
intravesical immunotherapy for early stage bladder cancer.
It is made from a weakened strain of Mycobacterium bovis, a vaccine for tuberculosis.Immunotherapy is used to prompt the immune system into attacking cancer cells. BCG is a liquid drug that can be deposited directly into your bladder through a catheter. Doctors have been using this method of treating superficial bladder cancer for 40 years.BCG is appropriate for non-invasive (stage 0) and minimally invasive (stage 1) bladder cancers. It usually follows a procedure called
transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT).
It is intended to help prevent recurrence. This treatment only affects cells
inside the bladder. It’s not useful for later stage bladder cancer that has
spread into or beyond the bladder lining, or to other tissues and organs.
Is there any preparation involved?
It is important that you follow your doctor’s instructions for what to do before and after the procedure. Tell your doctor about all the medications you take. Certain immunosuppressants, antimicrobial therapies, and radiation therapies can interfere with BCG treatment.
You will be advised to limit your fluid intake for four hours prior to the procedure. You might be told to avoid caffeine for a few hours longer than that, because it is a diuretic and could make things more difficult.
You’ll be asked to urinate just before the procedure, so you’ll be able to hold the medication in your bladder for several hours.
What happens during treatment?
A urinary catheter is inserted through your urethra and into your bladder. Then the BCG solution is injected into the catheter. The catheter is clamped off so the solution stays in your bladder. Some doctors may remove the catheter at this time.
You have to hold the medicine in your bladder. You’ll be instructed to lie on your back and to roll from side to side to make sure the solution reaches your entire bladder.
After about two hours, the catheter is unclamped so the fluid can be drained. If the catheter was already removed, you’ll be asked to empty your bladder at this time.
What can I expect following treatment?
For six hours after each treatment, you’ll have to be very careful when you urinate to avoid transmitting BCG to others. Men should urinate while seated to avoid splashing.
Disinfect the urine by adding 2 cups of bleach into the toilet. Let it stand for about 20 minutes before flushing. You should also wash your genital area very carefully after you urinate, so your skin doesn’t become irritated from the BCG. Wash your hands thoroughly, too.
Men can pass BCG to their partner during sex. For that reason, you should avoid sex for 48 hours after each treatment. Use a condom between treatments and for six weeks following your final treatment.
Women should avoid getting pregnant or breastfeeding while on BCG therapy.
Treatment is usually given every week for six weeks.
What side effects can occur?
One benefit of BCG is that while it affects the cells in your bladder, it doesn’t have a major effect on any other part of your body. But there can be a few side effects such as:
- fever
- chills
- fatigue
- a burning sensation in the bladder
- urinary urgency or frequent urination
- blood in the urine
Contact your doctor if you experience one of the above symptoms, have increasing pain or unable to urinate.